Competency Area 2: Crop Staging, Growth and Development
PO 7. Describe the systems used to stage forage legumes and grasses.
&
PO 8. Use the staging systems to identify growth stages of forage legumes and grasses.
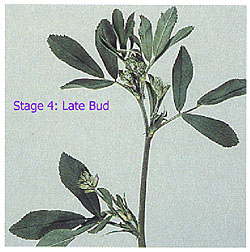
Alfalfa - Mean Stage by Count (see also http://css.cals.cornell.edu/cals/css/extension/upload/AlfalfaBulletin.pdf).
The mean stage of maturity by count (MSC) method consists of taking random, representative field samples, and scoring individual stems for stage of development. Stems in the vegetative stages are scored 0-2, bud stage 3-4, flowering 5-6, and seed production 7-9. The MSC is calculated as the weighted mean stage of all stems collected in the sample.
Click on images to enlarge
Perennial grass staging system
Perennial grass proceeds through a sequence of developmental stages: 1) germination, 2) vegetative; 3) elongation; 4) reproductive, and 5) seed ripening. The vegetative growth period is characterized by the development of leaves. Elongation is the period during which stem internodes elongate and is also referred to as jointing. During elongation the developing inflorescence pushes through the uppermost leaf sheath commonly referred to as boot stage. The reproductive stage is the period during which the developing inflorescence emerges and pollination occurs.
Information on quantifying growth stages can be found at (Moore et al. (1991) Describing and Quantifying Growth Stages of Perennial Forage Grasses. Agron. J. 83:1073). The five growth stages above have been related to a continuous numerical index. Germination stages are numbered from 0 to 0.9 and seed production stages are numbered from 4.0 to 4.9 on the numerical scale. Vegetative stages 1.0 to 1.9 start with emergence of first leaf and the index increases with each additional collared leaf. Elongation stages range from 2.0 to 2.9 starting with onset of elongation and the index increases with each additional palpable/visible node. The Reproductive stages range from 3.0 to 3.9 and start with boot stage. The emergence of the inflorescence through post-anthesis is included. Each stage of the system also has a mnemonic code (e.g. R1 = inflorescence emergence).
Primary and secondary growth stages and their numerical indices and descriptions for staging growth and development of perennial grasses.
Stage |
Index |
Description |
Germination |
||
G0 |
0.0 |
Dry seed |
G1 |
0.1 |
Imbibition |
G2 |
0.3 |
Radicle emergence |
G3 |
0.5 |
Coleoptile emergence |
G4 |
0.7 |
Mesocotyl and/or coleoptile elongation |
G5 from soil |
0.9 |
Coleoptile emergence from soil |
Vegetative-Leaf development |
||
VE or V0 |
1.0 |
Emergence of first leaf |
V1 |
(1/N)+0.9 |
First leaf collared |
V2 |
(2/N)+0.9 |
Second leaf collared |
Vn |
(n/N)+0.9 |
Nth leaf collared |
Elongation-Stem elongation |
||
E0 |
2.0 |
Onset of stem elongation |
E1 |
(1/N)+1.9 |
First node palpable/visible |
E2 |
(2/N)+1.9 |
Second node palpable/visible |
En |
(n/N)+1.9 |
Nth node palpable/visible |
Reproductive-Floral development |
||
R0 |
3.0 |
Boot stage |
R1 |
3.1 |
Inflorescence emergence/1st spikelet visible |
R2 |
3.3 |
Spikelets fully emerged/peduncle not emerged |
R3 |
3.5 |
Inflorescence emerged /peduncle fully elongated |
R4 |
3.7 |
Anther emergence/anthesis |
R5 |
3.9 |
Post anthesis/fertilization |
Seed development and ripening |
||
S0 |
4.0 |
Caryopsis visible |
S1 |
4.1 |
Milk |
S2 |
4.3 |
Soft dough |
S3 |
4.5 |
Hard dough |
S4 |
4.7 |
Endosperm hard/physiological maturity |
S5 |
4.9 |
Endosperm dry/seed ripe |
Quick Links
- Competency Area 1: Crop Adaptation
- Competency Area 2: Crop Staging, Growth, and Development
- Competency Area 3: Tillage Systems
- Competency Area 4: Seeding Factors
- Competency Area 5: Seeding Rates and Row Spacing
- Competency Area 6: Considerations in Replanting Decisions
- Competency Area 7: Forage Harvesting Factors
- Competency Area 8: Cropping Systems